Welcome to the cloudflare-operator documentation!
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
cloudflare-operator
- 1: Core Concepts
- 2: Get Started
- 3: Installation
- 4: Guides
- 4.1: Create DNS records from Ingress
- 4.2: Monitoring with Prometheus
- 4.3: Dynamic DNS with IP objects
- 4.4: Fetch IP from a Kubernetes object
- 5: Resources
- 6: API Reference
1 - Core Concepts
Architecture
cloudflare-operator is designed to serve as the single source of truth for Cloudflare DNS records.
It relies on the Kubernetes API to store the desired state of DNS records using Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs).
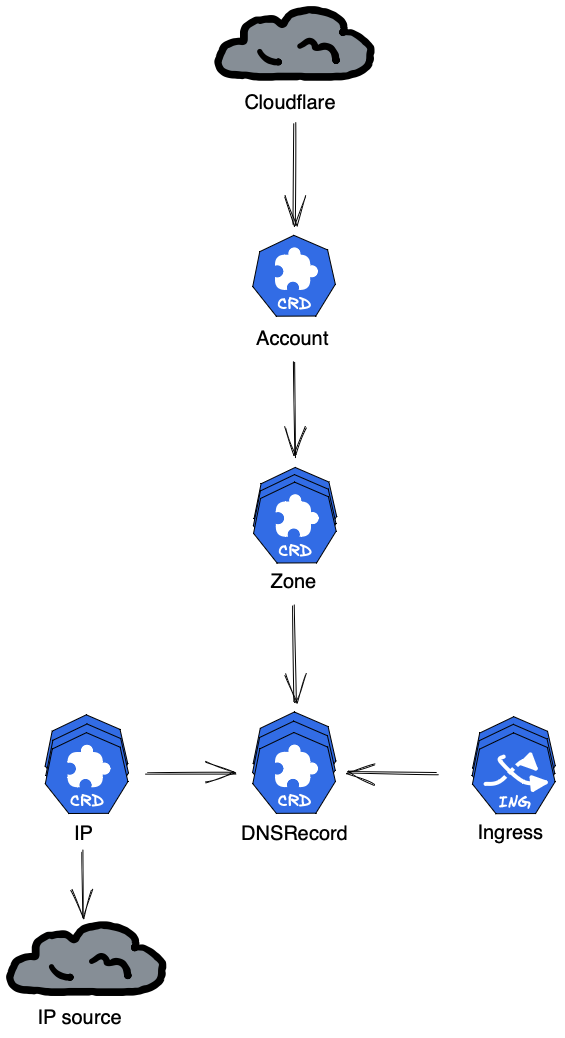
DNS records
Cloudflare DNS records are specified using a CRD (dnsrecords.cloudflare-operator.io).
These records can be created manually, through a GitOps workflow, or automatically generated from Kubernetes Ingress resources.
The Kubernetes API serves as the “single source of truth” for all zones in the configured Cloudflare account.
For more information on creating and using DNS records, please refer to the DNSRecords documentation.
IP objects
IP objects can be utilized to follow the “don’t repeat yourself” (DRY) principle.
DNS records can be configured to use an IP object as the target content.
If the IP object is updated, all DNS records that use it will be updated automatically.
The effective IP can either be configured in the IP object, or it can be dynamically fetched from the internet.
This enables you to use cloudflare-operator as a dynamic DNS controller.
Reconciliation
Reconciliation is the process of ensuring that the state of the cluster aligns with the desired state.
This process also incorporates “self-healing” by retrying failed operations after a specified interval.
2 - Get Started
This tutorial shows you how to get started with using cloudflare-operator and create a sample DNS record.
Before you begin
The following prerequisites are required to complete this tutorial:
- A Kubernetes cluster with cloudflare-operator installed (follow the installation guide)
- A Cloudflare account
Note that after a successful installation and configuration, cloudflare-operator will delete ALL DNS records in EVERY ZONE to which the API token has access!
It is therefore highly recommended to export your existing DNS records first!
Create Cloudflare API token
The token can be created by following this guide.
The following permissions are required:
Zone:Zone:ReadZone:DNS:Edit
Configure the following Zone resources:
Include:All zones
or, if you want to limit the zones to which the token has access:
Include:Specific zone:example.com
The summary should look similar to this:
All zones - Zone:Read, DNS:Edit
Configure Cloudflare account
Create a secret with the previously created Cloudflare API token.
The key in the secret must be named
apiToken.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
name: cloudflare-api-token
namespace: cloudflare-operator
stringData:
apiToken: 1234
Next, create an account object:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: Account
metadata:
name: account-sample
spec:
apiToken:
secretRef:
name: cloudflare-api-token
namespace: cloudflare-operator
Did you export your existing DNS records?
After creating the account, cloudflare-operator will delete ALL DNS records in EVERY ZONE to which the API token has access!
This is your last chance to export your existing DNS records!
Check if the account is ready:
kubectl get accounts.cloudflare-operator.io
This should output the following:
NAME READY
account-sample True
kubectl get zones.cloudflare-operator.io
NAME ZONE NAME ID READY
example-com example.com 12345678901234567890123456789012 True
Create a DNS record
Now, we can create our first DNS record:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: DNSRecord
metadata:
name: example-com
namespace: cloudflare-operator
spec:
name: example.com
type: A
content: 69.42.0.69
proxied: true
ttl: 1
interval: 5m0s
Check the status of the DNS record:
kubectl get dnsrecords.cloudflare-operator.io --namespace cloudflare-operator
NAME RECORD NAME TYPE READY
example-com example.com A True
3 - Installation
This guide walks you through installing cloudflare-operator.
Prerequisites
- Install Helm 3
- Kubernetes cluster
Install cloudflare-operator
Helm repository
Add the cloudflare-operator Helm chart repository:
helm repo add containeroo https://charts.containeroo.ch
Update the Helm chart repository:
helm repo update
Custom Resource Definitions
As per the Helm best practices, cloudflare-operator Helm chart doesn’t ship with CRDs.
To install the latest CRDs, run the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/containeroo/cloudflare-operator/releases/latest/download/crds.yaml
If you want to install a specific version of CRDs, run the following command:
export VERSION=x.y.z
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/containeroo/cloudflare-operator/releases/download/v${VERSION}/crds.yaml
Operator installation
Default installation
To install the latest version of cloudflare-operator, run the following command:
helm upgrade --install \
cloudflare-operator containeroo/cloudflare-operator \
--namespace cloudflare-operator \
--create-namespace
If you want to install a specific version of cloudflare-operator, run the following command:
export VERSION=x.y.z
helm upgrade --install \
cloudflare-operator containeroo/cloudflare-operator \
--namespace cloudflare-operator \
--create-namespace \
--version v${VERSION}
Customized installation
Create a values.yaml file.
A full list of all supported Helm values can be found here.
Example values.yaml file:
---
image:
repository: ghcr.io/containeroo/cloudflare-operator
tag: latest
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
Run the following command to install cloudflare-operator with the customized Helm values:
helm upgrade --install \
cloudflare-operator containeroo/cloudflare-operator \
--namespace cloudflare-operator \
--create-namespace \
--values values.yaml
4 - Guides
4.1 - Create DNS records from Ingress
cloudflare-operator can create DNS records from Ingress resources. This guide shows how to configure the controller to automatically create DNS records for your Ingress resources.
Ingress annotations
One of the following annotations is required: cloudflare-operator.io/content or cloudflare-operator.io/ip-ref
Ingress objects that do not have one of these annotations will be ignored by cloudflare-operator.
These are the available annotations:
| Annotation | Value | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
cloudflare-operator.io/content |
IP address or domain | DNS record content (e.g. 69.42.0.69) |
yes if ip-ref is not set |
cloudflare-operator.io/ip-ref |
Reference to an IP object | e.g. my-external-ip |
yes if content is not set |
cloudflare-operator.io/proxied |
true or false |
Whether the record should be proxied | no |
cloudflare-operator.io/ttl |
1 or 60 - 86400 |
TTL of the DNS record | no |
cloudflare-operator.io/type |
A, AAAA or CNAME |
Desired DNS record type | no |
cloudflare-operator.io/interval |
e.g. 5m0s |
Interval at which the DNSRecord object should be reconciled | no |
An example Ingress resource with annotations:
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
cloudflare-operator.io/type: CNAME
cloudflare-operator.io/content: example.com
name: blog
namespace: blog
spec:
rules:
- host: blog.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: blog
port:
name: http
path: /
pathType: Prefix
This will create a DNS record for the host blog.example.com with the content example.com and the type CNAME.
cloudflare-operator only supports
networking.k8s.io/v1 Ingresses.
4.2 - Monitoring with Prometheus
Prerequisites
The easiest way to deploy all the necessary components is to use kube-prometheus-stack.
Enable metrics
In order to enable metrics and automatically deploy the required resources, you need to reconfigure the Helm chart.
Create a values.yaml file with the following content:
---
metrics:
podMonitor:
enabled: true
prometheusRule:
enabled: true
Now you can install / upgrade the Helm chart by following the installation guide.
Install cloudflare-operator Grafana dashboard
# Download Grafana dashboard
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/containeroo/cloudflare-operator/master/config/manifests/grafana/dashboards/overview.json -O /tmp/grafana-dashboard-cloudflare-operator.json
# Create the configmap
kubectl create configmap grafana-dashboard-cloudflare-operator --from-file=/tmp/grafana-dashboard-cloudflare-operator.json
# Add label so Grafana can fetch dashboard
kubectl label configmap grafana-dashboard-cloudflare-operator grafana_dashboard="1"
Available metrics
For each cloudflare-operator.io kind, the controller exposes a gauge metric to track the status condition.
Ready status metrics:
cloudflare_operator_account_status
cloudflare_operator_dns_record_status
cloudflare_operator_ip_status
cloudflare_operator_zone_status
Alerting
The following alerting rule can be used to monitor DNS record failures:
groups:
- alert: DNSRecordFailures
annotations:
summary:
DNSRecord {{ $labels.name }} ({{ $labels.record_name }}) in namespace
{{ $labels.exported_namespace }} failed
expr: cloudflare_operator_dns_record_status > 0
for: 1m
labels:
severity: critical
4.3 - Dynamic DNS with IP objects
As described in the core concept, IP objects allow you to use cloudflare-operator as a dynamic DNS controller.
In this guide, we will configure an IP object to fetch the public IP address from the internet and use it as the target content for a DNS record.
Simple example
Create an IP object with the following content:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: IP
metadata:
name: external-v4
spec:
ipSources:
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://ifconfig.me/ip
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://ipecho.net/plain
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://myip.is/ip/
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://checkip.amazonaws.com
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://api.ipify.org
type: dynamic
interval: 5m0s
The IP object will fetch the public IP address from the internet using one of the specified URLs.
If the request fails, the next URL will be tried. If all URLs fail, the last known IP will be used and
the ready condition will be set to false.
Now, create a DNS record object with the following content:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: DNSRecord
metadata:
name: example-com
namespace: cloudflare-operator
spec:
name: example.com
ipRef:
name: external-v4 # reference to the IP object
proxied: true
ttl: 1
type: A
Response filtering
Using jq
You can use jq to filter the response content.
Here is an example for ipify.org:
Request content:
$ curl 'https://api.ipify.org?format=json'
{"ip":"69.42.0.69"}
The IP object would look like this:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: IP
metadata:
name: external-v4
spec:
ipSources:
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://api.ipify.org?format=json
responseJQFilter: .ip
type: dynamic
interval: 5m0s
Using regex
If you want to use a regex, you can use the postProcessingRegex field.
This might be useful if you want to extract the IP address from a HTML page.
The regex must contain a single capture group.
Here is an example for ifconfig.me:
Request content:
$ curl 'https://ifconfig.me/'
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<html>
...
In this case, the IP object would look like this:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: IP
metadata:
name: external-v4
spec:
ipSources:
- requestMethod: GET
url: https://ifconfig.me/
postProcessingRegex: '(\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})'
type: dynamic
interval: 5m0s
Fetching IP from an API
If you want to fetch the IP address from an API, you can use the responseJQFilter field.
In this example, we are going to fetch the IP from a Hetzner cloud instance.
To authenticate with the API, you can configure the IP object to use a secret
where the secret key will be used as the header name
and the secret value will be used as the header value.
Create a secret with the following content:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: hetzner-cloud-api-key
namespace: cloudflare-operator
stringData:
Authorization: Bearer <your-api-token>
Now, create an IP object with the following content:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: IP
metadata:
name: my-instance-v4
spec:
ipSources:
- requestHeaders:
Accept: application/json
requestHeadersSecretRef:
name: hetzner-cloud-api-key
namespace: cloudflare-operator
requestMethod: GET
responseJQFilter: .servers[] | select(.name == "my-instance.example.com").public_net.ipv4.ip
url: https://api.hetzner.cloud/v1/servers
type: dynamic
interval: 5m0s
4.4 - Fetch IP from a Kubernetes object
If you have a Kubernetes object that contains an IP address, you can use cloudflare-operator to fetch the IP address from the object and use it as the target content for a DNS record.
This can be useful if you are using Istio or want to fetch the IP from a Kubernetes service.
This guide will show you how to configure an IP object to fetch the IP address from a Kubernetes service.
Operator configuration
Add a kubectl sidecar to the operator pod by using the following Helm values:
sidecars:
- name: proxy
image: bitnami/kubectl
args: ["proxy", "--port=8858"]
The operator will need additional permissions to access services.
In order to grant the operator these permissions, add the following Helm values:
clusterRole:
extraRules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
Install or update the Helm chart using this guide.
IP object
An IP object could then look like this:
---
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: IP
metadata:
name: ingress-ip
spec:
type: dynamic
ipSources:
- url: localhost:8858/api/v1/namespaces/ingress-nginx/services/ingress-nginx
responseJQFilter: ".status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip"
This IP object will fetch the IP address from the Kubernetes service ingress-nginx in the namespace ingress-nginx using the kubectl proxy.
5 - Resources
5.1 - Account
The API specification can be viewed here.
In order to use cloudflare-operator, you need to create an account resource. This resource contains the credentials for the Cloudflare API.
Learn more about the account resource in the getting started guide.
5.2 - Zone
The API specification can be viewed here.
Zone resources represent the zones available in the Cloudflare account. They are used to store the zone id and are fully managed by cloudflare-operator.
Therefore, you should not create or modify zone resources manually.
5.3 - DNSRecord
The API specification can be viewed here.
DNSRecord resources represent DNS records in the Cloudflare account.
For each DNS record, you need to create a DNSRecord resource.
cloudflare-operator will create the DNS record in the Cloudflare account and keep it in sync with the DNSRecord resource.
As described in this guide, cloudflare-operator can creaet DNSRecords from Ingress resources.
If you want to create DNSRecords manually, you can use the following example as a starting point:
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: DNSRecord
metadata:
name: vpn
namespace: cloudflare-operator
spec:
name: vpn.example.com
type: A
ipRef:
name: dynamic-external-ipv4-address
proxied: false
ttl: 120
interval: 5m0s
This example creates a DNS record for the domain vpn.example.com with the type A and the IP address from the dynamic-external-ipv4-address IP object.
It also sets the proxied flag to false and the ttl to 120.
Another example is the following:
apiVersion: cloudflare-operator.io/v1
kind: DNSRecord
metadata:
name: blog
namespace: cloudflare-operator
spec:
name: blob.example.com
content: 69.42.0.69
type: A
proxied: true
ttl: 1
interval: 5m0s
This example creates a DNS record for the domain blog.example.com with the type A and the content 69.42.0.69.
5.4 - IP
The API specification can be viewed here.
As described in the core concept, IP objects can be used to follow the “don’t repeat yourself” (DRY) principle.
They also allow you to use the same IP address in multiple DNS records and let you use cloudflare-operator as a dynamic DNS service.
Learn more about the usage of IP objects in the dynamic DNS guide.
6 - API Reference
Packages:
cloudflare-operator.io/v1
Package v1 contains API Schema definitions for the source v1 API group
Resource Types:Account
Account is the Schema for the accounts API
| Field | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
metadataKubernetes meta/v1.ObjectMeta |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the
metadata field.
|
||||||
specAccountSpec |
|
||||||
statusAccountStatus |
AccountSpec
(Appears on: Account)
AccountSpec defines the desired state of Account
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
apiTokenAccountSpecApiToken |
Cloudflare API token |
intervalKubernetes meta/v1.Duration |
(Optional)
Interval to check account status |
managedZones[]string |
(Optional)
List of zone names that should be managed by cloudflare-operator |
AccountSpecApiToken
(Appears on: AccountSpec)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
secretRefKubernetes core/v1.SecretReference |
Secret containing the API token (key must be named “apiToken”) |
AccountStatus
(Appears on: Account)
AccountStatus defines the observed state of Account
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
conditions[]Kubernetes meta/v1.Condition |
(Optional)
Conditions contains the different condition statuses for the Account object. |
zones[]AccountStatusZones |
(Optional)
Zones contains all the zones of the Account |
AccountStatusZones
(Appears on: AccountStatus)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
namestring |
(Optional)
Name of the zone |
idstring |
(Optional)
ID of the zone |
DNSRecord
DNSRecord is the Schema for the dnsrecords API
| Field | Description | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
metadataKubernetes meta/v1.ObjectMeta |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the
metadata field.
|
||||||||||||||||||
specDNSRecordSpec |
|
||||||||||||||||||
statusDNSRecordStatus |
DNSRecordSpec
(Appears on: DNSRecord)
DNSRecordSpec defines the desired state of DNSRecord
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
namestring |
DNS record name (e.g. example.com) |
contentstring |
(Optional)
DNS record content (e.g. 127.0.0.1) |
ipRefDNSRecordSpecIPRef |
(Optional)
Reference to an IP object |
typestring |
(Optional)
DNS record type |
proxiedbool |
(Optional)
Whether the record is receiving the performance and security benefits of Cloudflare |
ttlint |
(Optional)
Time to live, in seconds, of the DNS record. Must be between 60 and 86400, or 1 for ‘automatic’ (e.g. 3600) |
dataKubernetes pkg/apis/apiextensions/v1.JSON |
(Optional)
Data holds arbitrary key-value pairs used to further configure the DNS record |
priorityuint16 |
(Optional)
Required for MX, SRV and URI records; unused by other record types. Records with lower priorities are preferred. |
intervalKubernetes meta/v1.Duration |
(Optional)
Interval to check DNSRecord |
DNSRecordSpecIPRef
(Appears on: DNSRecordSpec)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
namestring |
(Optional)
Name of the IP object |
DNSRecordStatus
(Appears on: DNSRecord)
DNSRecordStatus defines the observed state of DNSRecord
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
conditions[]Kubernetes meta/v1.Condition |
(Optional)
Conditions contains the different condition statuses for the DNSRecord object. |
recordIDstring |
(Optional)
Cloudflare DNS record ID |
IP
IP is the Schema for the ips API
| Field | Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
metadataKubernetes meta/v1.ObjectMeta |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the
metadata field.
|
||||||||
specIPSpec |
|
||||||||
statusIPStatus |
IPSpec
(Appears on: IP)
IPSpec defines the desired state of IP
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
addressstring |
(Optional)
IP address (omit if type is dynamic) |
typestring |
(Optional)
IP address type (static or dynamic) |
intervalKubernetes meta/v1.Duration |
(Optional)
Interval at which a dynamic IP should be checked |
ipSources[]IPSpecIPSources |
(Optional)
IPSources can be configured to get an IP from an external source (e.g. an API or public IP echo service) |
IPSpecIPSources
(Appears on: IPSpec)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
urlstring |
(Optional)
URL of the IP source (e.g. https://checkip.amazonaws.com) |
requestBodystring |
(Optional)
RequestBody to be sent to the URL |
requestHeadersKubernetes pkg/apis/apiextensions/v1.JSON |
(Optional)
RequestHeaders to be sent to the URL |
requestHeadersSecretRefKubernetes core/v1.SecretReference |
(Optional)
RequestHeadersSecretRef is a secret reference to the headers to be sent to the URL (e.g. for authentication) where the key is the header name and the value is the header value |
requestMethodstring |
RequestMethod defines the HTTP method to be used |
responseJQFilterstring |
(Optional)
ResponseJQFilter applies a JQ filter to the response to extract the IP |
postProcessingRegexstring |
(Optional)
PostProcessingRegex defines the regular expression to be used to extract the IP from the response or a JQ filter result |
insecureSkipVerifybool |
(Optional)
InsecureSkipVerify defines whether to skip TLS certificate verification |
IPStatus
(Appears on: IP)
IPStatus defines the observed state of IP
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
conditions[]Kubernetes meta/v1.Condition |
(Optional)
Conditions contains the different condition statuses for the IP object. |
lastObservedIPstring |
(Optional)
LastObservedIP contains the IP address observed at the last interval (used to determine whether the IP has changed) |
Zone
Zone is the Schema for the zones API
| Field | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
metadataKubernetes meta/v1.ObjectMeta |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the
metadata field.
|
||||||
specZoneSpec |
|
||||||
statusZoneStatus |
ZoneSpec
(Appears on: Zone)
ZoneSpec defines the desired state of Zone
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
namestring |
Name of the zone |
idstring |
ID of the zone |
intervalKubernetes meta/v1.Duration |
(Optional)
Interval to check zone status |
ZoneStatus
(Appears on: Zone)
ZoneStatus defines the observed state of Zone
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
conditions[]Kubernetes meta/v1.Condition |
(Optional)
Conditions contains the different condition statuses for the Zone object. |
This page was automatically generated with
gen-crd-api-reference-docs